- mail@thehubq.com
- +974 6685 1887
Network cabling
Network cabling is one of the most important aspects in any network infrastructure and has become increasingly critical with the introduction of newer technologies such as blade servers, virtualization, network storage devices, wireless access points and more. Network services such as file sharing, Internet access, network printing, email, ERP systems and more, are all delivered to the end users via the network infrastructure, which usually includes switches, fiber optic links and of course UTP cabling. This series will focus on the different type of Ethernet copper cabling specifications, speeds and caveats of each technology.

Termination and Testing Patch panel
In an enterprise network, a patch panel serves as a sort of static switchboard, using cables to interconnect network computers within a LAN and to outside lines including the internet or other wide area networks (WANs). Patch panels can also be used to interconnect and manage fiber optic cables..
Patch Panel is a device that has a number of same or similar kinds of jacks; the purpose of the jacks are connecting and routing circuits to interconnect monitor and test the circuits so that it can be ensured that the circuits are working in flexible and user-friendly manner.

Racks and switches supply and installations
Racks organize IT equipment, such as servers and network switches,
into standardized assemblies that make efficient use of space and other
resources. Depending on the options you choose, they can also improve
power protection, cooling, cable management, device management,
physical security, mobility, ease of installation and protection from harsh
environmental conditions.
Choosing the right racks and configuring them to match your needs will
ensure that your IT equipment operates reliably and efficiently, saving
your organization from costly downtime and other needless expenses.

IP Telephony
Internet Protocol Telephony (IP Telephony) is the use of IP-based networks to build, provide and access voice, data or other forms of telephonic communications. IP telephony provides traditional telephonic communication over an IP-based network, the Internet - via an Internet service provider (ISP) - or directly from a telecommunications service provider.
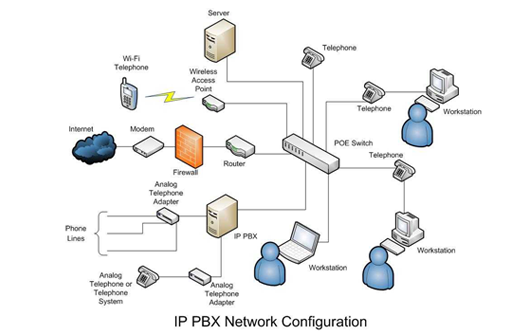
PABX system installation and configuration
Private Automatic Branch exchange (PABX) is an in-house telephone switching system which makes connections among the internal telephones of a private organization (or an enterprise) and also connects them to the public telecom network via various interfaces. ... Initially, Private branch exchanges used analog technology.